
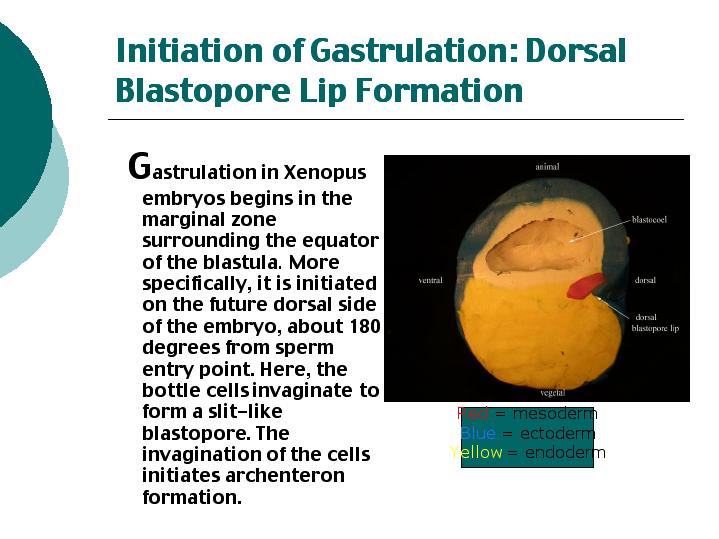
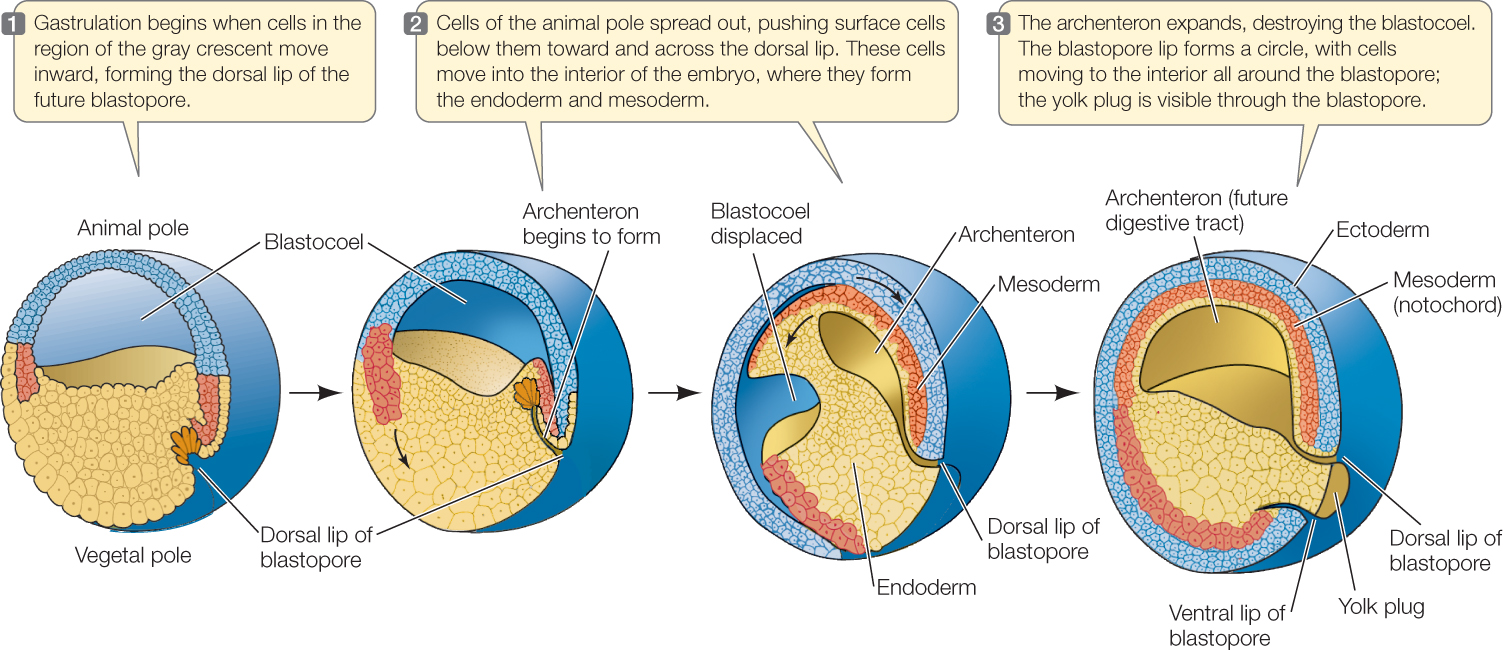
The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. Gastrulation is the stage in the early embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula (a single-layered hollow sphere of cells) is reorganized into a multilayered structure known as the gastrula. The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. Principles of Inheritance and Variation.New Questions and Answers and Forum Categories Hyman (1940) has stated that all multicellular animals have evolved from some single-called protest, probably from a colonial flagellate and some advanced phyla which are grouped as protostomes and deuterostomes, originate separately through the trochophore and dipleurula larva. According to him, the evidences of phylogenetic relationship between echinoderms hemichordates and chordates are very convincing on the basis of larval stages.
Recent molecular data such as 18SrRNA and mitochondrial DNA gene sequences of lophophorate phyla indicate that they (e.g., Phoronids, Brachiopods and Ectoprocts) place in the protostomes.īarnes (1987) has suggested that chordates evolved from non-chordata group and hypothetical echinoderm larva (dipleurula) and other echinoderm larvae hold the key position. The echinoderms, hemichordates and chordates share some common features such as gill slits (absent in living echinoderms but are found in fossil carpoids), protocoelic nephridium (present in echinoderms and hemichordates but in chordates it has secondarily lost).Īll the five mentioned groups are included under deuterostomes on the basis of embryonic development features. With these groups, the other few minor groups such as lophophorates and chaetognaths are included under deuterostomes but in considerable controversy. The deuterostomes include Echinodermata, Hemichordata and Chordata. Lophotrochozoa, e.g., Molluscs and Annelids. Ecdysozoa, e.g., Arthropods and Nematodes (pseudocoelomates)Ģ. The absence of segmentation in echiurans, sipunculans and molluscs is a secondary loss (Ruppert and Barnes, 1994).īased on current molecular data, it has been suggested that the coelomate protostome animals can be divided into 2 groups:ġ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
